Intel Core Ultra 9 285K Benchmark: 18% Performance Boost Over 14900K Explained

Intel Core Ultra 9 285K Benchmark: A Sneak Peek into the Future of Arrow Lake-S Desktop CPUs
Intel has been making waves within the tech world with its up-and-coming Intel Core Ultra 9 285K, the lead CPU from the unused Bolt Lake-S desktop lineup. As of late, the primary benchmarks of this much-anticipated processor were spilled by a source known as Jaykihn, and the results seem promising. The Intel Core Ultra 9 285K is being hailed for its impressive multi-thread execution advancements, which are anticipated to supply a competitive edge over past Intel CPUs and its key equal, AMD’s Ryzen processors.
In this post, we’ll jump into the points of interest of the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K benchmark spills, analyze the execution picks up, and see what these come about for clients.
Specifications of the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K
Sometime recently we dived into the benchmarks, let’s begin with taking a see at the determinations of Intel’s core Ultra 9 285K CPU. As a portion of the Bolt Lake-S lineup, this processor brags noteworthy enhancements in both design and execution measurements.
The Intel Core Ultra 9 285K is based on Intel’s modern Bolt Lake-S design and comes with a 24-core/24-thread arrangement (8 Execution centers and 16 Effectiveness centers). The Execution centers (P-cores) run at a base clock of 3.7 GHz and can boost up to 5.7 GHz, whereas the Productivity centers (E-cores) work between 3.2 GHz and 4.6 GHz. This CPU is prepared with 36 MB of L3 cache and runs at a TDP of 125W, with the capacity to slope up to 250W amid overwhelming workloads.
Intel’s choice to go with TSMC’s N3B process node (even though a few guess it might be Intel’s possess 20A) could be a step towards moving forward vitality proficiency and accomplishing higher clock speeds, particularly in comparison to the earlier Center i9-14900K, which was based on Intel’s 7nm hub.
| Specification | Core Ultra 9 285K | Core i9-14900K | Core i9-13900K | AMD Ryzen 9 9950X |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Arrow Lake-S (Lion Cove/Skymont) | Raptor Lake-S | Raptor Lake-S | Zen 5 |
| Cores/Threads | 24 (8P+16E) / 24 | 24 (8P+16E) / 32 | 24 (8P+16E) / 32 | 16 / 32 |
| Base Clock (P/E Core) | 3.7 / 3.2 GHz | 3.2 / 2.4 GHz | 3.0 / 2.2 GHz | 4.0 GHz |
| Max Boost Clock (P/E Core) | 5.7 / 4.6 GHz | 6.0 / 4.4 GHz | 5.8 / 4.3 GHz | 5.7 GHz |
| All-Core Boost (P/E Core) | 5.4 / 4.6 GHz | 5.5 / 4.2 GHz | 5.4 / 4.1 GHz | 5.2 GHz |
| Cache (L3) | 36 MB | 36 MB | 36 MB | 64 MB |
| TDP (PL1) | 125W | 125W | 125W | 170W |
| Max Power Draw (PL2) | 250W | 253W | 253W | 230W |
| Cinebench R23 Multi-Core Performance | +18% over 14900K | Reference Score | Slightly behind | Comparable (Stock) |
| Single-Core Performance | Similar to 14900K | Reference Score | Slightly behind | Comparable (Stock) |
Benchmark Results: Performance Uplift in Multi-Threaded Tasks
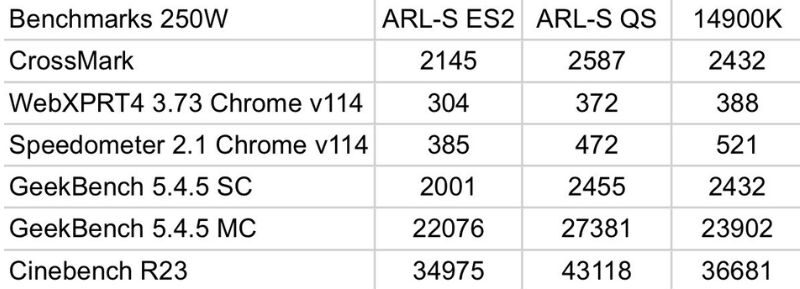
One of the foremost energizing angles of the spilled benchmarks is the 18% performance elevate in multi-threaded workloads. This execution pick-up was measured in Cinebench R23, a well-known benchmarking device utilized to assess CPU execution in real-world rendering errands. When running at 250W, the Intel core Ultra 9 285K is overseen to beat the Center i9-14900K, a processor known for its solid multi-threaded capabilities.
The Cinebench R23 score places the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K immovably ahead of its forerunner and indeed puts it in coordinate competition with AMD’s up-and-coming Ryzen 9 9950X “Zen 5” chip. The Ryzen 9 9950X is additionally anticipated to be a multi-threaded powerhouse, but it runs at around 170W, altogether lower than the 250W utilized by the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K in these tests. Despite this, Intel’s 18% execution boost gives it an edge, making it a beat contender for clients who prioritize multi-threaded workloads like video altering, 3D rendering, and complex reenactments.
Single-Core Performance: Consistent with the Core i9-14900K

While the multi-threaded execution saw a recognizable change, the single-core execution was not as sensational. Based on the comes about from Geekbench 5, the single-core execution of the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K was almost the same as the Center i9-14900K, which boosts up to 5.8 GHz.
It is critical to note that Geekbench 5 measures execution over distinctive workloads, and single-core execution can change depending on the application. Furthermore, components such as memory arrangements (e.g., DDR5 speeds) and whether the test was boosting as planning can influence single-core scores.
Despite this, the reliable execution in single-threaded errands shows that whereas the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K may not be revolutionizing single-core execution, it holds its possession against Intel’s as of now amazing 14900K.
Energy Efficiency and Thermal Management
The Intel Core Ultra 9 285K is planned to adjust control utilization and execution, with a TDP of 125W in ordinary conditions and the capacity to thrust up to 250W amid overwhelming workloads. For comparison, the Center i9-14900K incorporates a top PL2 rating of 253W, so Intel has overseen packing more execution into a comparative control envelope.
Intel has centered on warm administration and vitality productivity, as demonstrated by the utilization of TSMC’s N3B handle hub. This progressed creation innovation is outlined to optimize control utilization and permit higher clock speeds without essentially expanding warm yield. This ought to lead to superior performance-per-watt, making the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K an appealing alternative for gamers, experts, and substance makers who require capable CPUs without intemperate warm or control utilization.
Intel’s Arrow Lake-S Lineup: What’s Coming?
The Intel Core Ultra 9 285K is anticipated to be a portion of Intel’s Bolt Lake-S desktop lineup, which is set to dispatch in October 2024. Together with the 285K, Intel will moreover discharge the Intel Core Ultra 7 265K and Intel Core Ultra 5 245K, all of which can be open CPUs congruous with Z890 motherboards highlighting the unused LGA 1851 attachment.
These motherboards will offer improved highlights, such as DDR5 memory bolster, PCIe 5.0 paths, and more progressed control conveyance frameworks, permitting clients to completely use the control of Intel’s unused chips.
Conclusion: Intel Core Ultra 9 285K Benchmark Overview
The early benchmarks of the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K show that Intel is on track to provide a strong execution update with its Bolt Lake-S lineup. With an 18% elevate in multi-threaded errands and competitive single-core execution, the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K looks set to outpace the Center i9-14900K and challenge AMD’s next-gen Ryzen 9 9950X.
This CPU will likely be a favorite among devotees who require tall multi-core execution for requesting errands, but gamers and common clients will too advantage of the made strides in vitality productivity and reliable single-core comes about. As the Bolt Lake-S lineup approaches its discharge, we can anticipate more refinements in clock speeds and execution, making Intel’s core Ultra 9 285K a lead to be careful for in 2024.
Click Here To Learn About:
- Lenovo Legion Pro 7 Reviews: Is This Best For Job, Games, Content Creators?
- AMD Zen 5: Unveiling Next-Gen Performance with Ryzen AI 300 Series
FAQs for Intel Core Ultra 9 285K
1. How does the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K compare to the Core i9-14900K?
The Intel Core Ultra 9 285K offers up to an 18% advancement in multi-threaded tasks compared to the Center i9-14900K, with comparable single-core execution. It too contains a more progressed engineering and better power effectiveness.
2. What is the power consumption of the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K?
The CPU includes a base TDP of 125W but can go up to 250W amid overwhelming workloads, comparable to the Center i9-14900K.
3. When is the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K expected to be released?
The Intel core Ultra 9 285K is anticipated to be dispatched in October 2024 as a portion of Intel’s Bolt Lake-S desktop lineup.

![Jabra Evolve 75- Everything You Need To Know [2024] Jabra Evolve 75](https://mediatalky.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Jabra-Evolve-75-768x576.jpg)




